In the realm of electrical engineering and circuit design, the selection of a Circuit Board Breaker is a critical decision that can significantly impact the performance and safety of your project. A Circuit Board Breaker serves as a protective device, interrupting the flow of electricity when it detects an overload or short circuit, thereby safeguarding both the circuit and the components involved. Choosing the right breaker involves a careful consideration of various factors to ensure optimal functionality and reliability.
When embarking on a project, understanding the specific requirements of your circuit is essential. Different applications may demand varying current ratings, voltage tolerances, and physical dimensions of Circuit Board Breakers. Additionally, the intended environment—ranging from temperature fluctuations to exposure to moisture—can influence your choice. By familiarizing yourself with the technical specifications and operational characteristics of these breakers, you can make a more informed selection that aligns with your project goals.
Moreover, integrating a suitable Circuit Board Breaker not only enhances the safety of the system but also contributes to the longevity and efficiency of the circuit. As projects evolve, staying abreast of the latest innovations and best practices in circuit protection will further empower you to make decisions that foster both resilience and performance in your designs.
Circuit board breakers play a crucial role in protecting electronic systems from overloads and short circuits. Understanding the various types of circuit board breakers is essential for making informed decisions in any electronic project. The two primary categories include thermal breakers and magnetic breakers. Thermal breakers respond to changes in temperature, providing protection by tripping when excessive heat is detected due to overcurrent. On the other hand, magnetic breakers operate instantaneously, tripping immediately upon experiencing a short circuit, making them ideal for applications where rapid response is critical.
In addition to the fundamental types, circuit board breakers come in various configurations suited for specific applications. For example, some are designed for low-voltage environments, making them suitable for consumer electronics, while others are built for higher voltage systems, often used in industrial settings. Factors such as the operating environment, required response time, and load characteristics must all be considered to select the appropriate breaker. By evaluating these types and applications, project designers can ensure optimal protection and functionality for their electronic circuits.
This bar chart illustrates the various types of circuit board breakers along with their common applications. Understanding these applications can help you choose the right breaker for your project.
When selecting a circuit board breaker for your project, several key specifications must be taken into account to ensure optimal performance and safety. One of the primary factors is the current rating, which should meet the demands of the specific application. According to industry standards, selecting a breaker with a current rating that exceeds the maximum expected load by at least 25% is advisable. This consideration helps mitigate the risk of nuisance tripping during transient conditions, which can occur in many electronic applications.
Another critical specification to consider is the voltage rating. The circuit board breaker must be adequately rated for the voltage levels present in your system. Reports indicate that failures in circuit protection often arise from mismatched voltage ratings, which can lead to dangerous short circuits or equipment damage. A voltage rating that exceeds your operating conditions can enhance reliability and provide a safety buffer against voltage spikes. Additionally, compatibility with various types of loads—such as resistive, inductive, or capacitive—is essential, as different load types may require specific breaker technologies to function effectively without degradation.
Thermal characteristics are also essential when choosing a breaker. Understanding the thermal response of the breaker under different load conditions can help design more efficient and safer circuits. According to recent studies, circuit breakers rated for higher thermal performance can reduce the risk of thermal overload, which is particularly vital in densely packed electronic assemblies. Selecting a circuit board breaker that can withstand the anticipated thermal environment is crucial for long-term reliability and performance in any application.
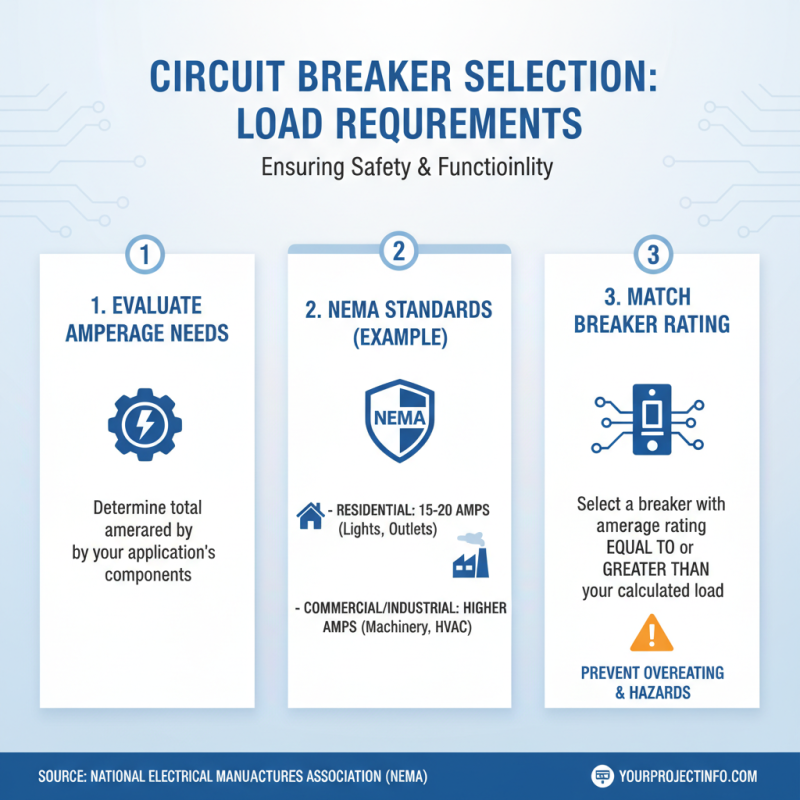
When selecting a circuit board breaker for your project, understanding the load requirements is paramount. Start by evaluating the amperage needs of your application. According to a report by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), most residential and commercial circuits require a specific amperage rating to prevent overheating and potential hazards. For instance, typical residential circuits often fall between 15 to 20 amps, while industrial applications may demand higher ratings depending on the equipment being used. Ensuring that the breaker can handle the required amperage will help to guarantee safety and functionality.
Next, consider the voltage specifications. The voltage rating must align with the system's operational demands to prevent insulation breakdown or equipment failure. The IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) standard recommends that circuit breakers are selected with a voltage rating that is at least 20% higher than the circuit’s operating voltage. This precaution provides an additional safety margin, accounting for potential voltage spikes that can occur in electrical systems.
Lastly, short-circuit ratings, also known as the interrupting capacity, are critical in determining a breaker’s ability to withstand fault conditions. According to research from the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), it is essential to choose a breaker with an interrupting capacity that exceeds the maximum prospective short-circuit current. This ensures that the circuit board breaker can effectively cut off power during fault conditions, minimizing damage to both the circuit and connected devices. Assessing these load requirements—amperage, voltage, and short-circuit ratings—ensures the right circuit board breaker is chosen for optimal performance and safety in any electrical project.
When selecting a circuit board breaker, environmental considerations play a crucial role that can impact both the project’s efficiency and its compliance with regulatory standards. The increasing emphasis on sustainability in the electronics industry highlights the need for selecting breakers that not only ensure safety but also minimize environmental impact. According to a report by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), using circuit breakers with eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient designs can reduce overall resource consumption by up to 20%. This aligns with global efforts to meet stricter environmental regulations, particularly in the European market, where directives such as RoHS and WEEE mandate the reduction of hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment.
One important tip when choosing circuit breakers is to consider their operational temperature range and their potential impact on energy efficiency. Breakers that are rated to operate effectively in varying temperatures can help reduce energy losses, which translates to lower carbon emissions during the lifespan of the circuit. Additionally, opting for circuit breakers that are designed for higher energy efficiency can significantly contribute to energy conservation efforts. Research indicates that energy-efficient circuit breakers can save businesses approximately 15-30% on energy costs annually, a compelling statistic that advocates for an environmentally conscious approach in selection.
Furthermore, you should assess the lifecycle of the circuit breaker, including its manufacturing, usage, and disposal processes. Prioritizing products that boast a longer lifespan and utilize recyclable materials can make a substantial difference in reducing electronic waste. According to statistics from the Global E-waste Monitor, the world generated around 53.6 million metric tons of e-waste in 2019, underscoring the urgent need for eco-friendly practices. By integrating environmental considerations into the selection process, you not only enhance the project's sustainability but also align with industry trends that benefit both the planet and your bottom line.
When selecting a circuit board breaker for your project, understanding regulatory standards and compliance is paramount. Circuit board breakers are essential components that protect electrical circuits by interrupting the flow in case of overloads or faults. Therefore, they must adhere to specific standards set by regulatory bodies to ensure safety and reliability. Familiarity with these standards aids in selecting breakers that not only protect your circuitry but also meet legal and safety requirements.
Regulatory compliance involves thorough knowledge of local and international standards, such as those established by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) or Underwriters Laboratories (UL). Depending on your project's location, you may also need to consider additional certifications or regulations. Ensuring your circuit board breaker meets these criteria can mitigate risks associated with equipment failure and enhance the overall safety of your project. Always verify that the selected breakers have appropriate testing and certification markings before proceeding, as this reflects their ability to operate safely within their specified parameters.